We have studied that as the voltage across reverse bias PN junction increase to certain value, called breakdown voltage, high reverse current is caused by which may damage the junction diode.
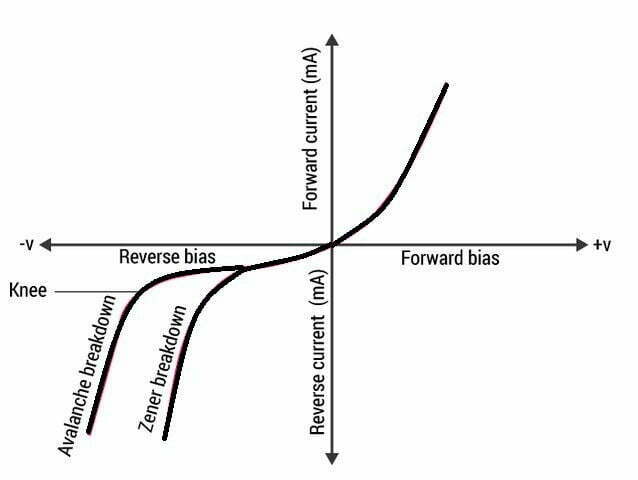
Before studying the difference between Avalanche breakdown and Zener breakdown we have to study two mechanism by which breakdown can occur, when PN junction is Reverse biased:
- Avalanche breakdown.
- Zener breakdown.
Contents
Avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown it is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting conducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow a very large currents within materials which are otherwise good insulators.
It is a type of electron Avalanche. The avalanche process occur when the carriers in the transition region are accelerated by the electric field to energy sufficient to free electron-hole pairs via collisions with bound electrons.
Avalanche breakdown is usually destroys ordinary diodes, but Avalanche diodes are designed to break-down this way at low voltage and can survive the reverse current. When a PN junction is reversed biased, the minority carriers (in p-region and n-region) flowing through the junction acquire kinetic energy under the effect of electric field across the junction.
The kinetic energy increases with the increase in reverse voltage. At a particular high reverse voltage, the kinetic energy of minority carriers becomes so high that they are able to Knock out electrons from the covalent bonds of the semiconductor material.
These liberated electrons in turn liberate more electrons from the covalent bonds. The effect is accumulative and hence a large amount of current is caused by breakdowns the crystal structure of the material.
This mechanism is known as Avalanche breakdown. This type of breakdown occurs in lightly doped PN junction.
Zener Breakdown
When a pn junction is reverse – biased, the depletion layer is widened and the potential barrier is increased with the increase in reverse voltage. The electric field across the junction is also increased to a high value. This large electric field break some of the covalent bond in p and n regions, leading to production of more and more electron-hole pairs.
These electron-hole pairs diffuse through junction and hence a large reverse current flows through the junction diode. This mechanism of increasing reverse current is known as Zener Breakdown.
The reverse voltage at which Zener breakdown occurs is known as Zener voltage and current corresponding to it is known as Zener current. This type of breakdown occur in heavily doped PN junction.
Difference between Avalanche breakdown and Zener breakdown
| Avalanche breakdown | Zener breakdown |
| The effect is accumulative and hence a large amount of current is caused by breakdowns the crystal structure of the material is called an avalanche breakdown. | The mechanism of increasing reverse current is known as Zener breakdown. |
| Valence electrons are pushes conduction due to the energy difference created by accelerated electrons, which gain their velocity due to their collision with other atoms. | The valence electrons are pulled into conduction due to the high electric field in the narrow depletion region. |
| When we increase the temperature there is increases in the breakdown voltage. | When we increase the temperature there is decreases in the breakdown voltage. |
| The VI characteristic curve is not as sharp as compare to the Zener breakdown. | It has a sharp curve of the VI characteristics. |
| This type breakdown occurs in a lightly doped p-n junction. | This type breakdown occurs in a heavily doped p-n junction. |
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is avalanche breakdown?
It is a type of electron avalanche occurs when the carriers in the transition region are accelerated by the electric field to energy sufficient to free electron-hole pairs via collisions with bound electrons.
Zener breakdown occurs.
This type of breakdown occur in heavily doped PN junction.
