Divergence and Curl of magnetic field
Divergence of Magnetic Field

We know, the magnetic field produced by a current element Id L vector at a point P (x,y,z) whose distance from the current element r is given by

Therefore, the magnetic field at P due to the whole current loop is given by


Taking divergence both sides, we get





We know curl of gradient is zero.

Using eqns. (4) and (5), eqn. (3) becomes

Thus, divergence of B vector is zero.
Any vector whose divergence is zero is known as a solenoidal vector. Thus, magnetic field vector B vector is a solenoidal vector.
This is the proof of Divergence of magnetic field.
Curl of Magnetic Field

Let us consider a region of space in which currents are flowing, the current density J vector varies from point to point but is time-independent.
The total steady current I is given by

where J vector is the current density of an element dS vector of the surface S bounded by the closed path.


But according to Stokes theorem, the closed line integral of the B vector is equal to the surface integral of its curl.

From (2) and (3)
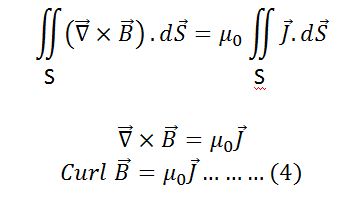
Which is the differential form of ampere’s law or curl of a magnetic field.